
The main window
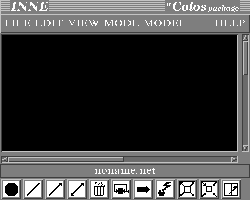
The application main window is opened when INNE is run and allows users to define the network
layout and architecture and to compute with it. The editing facilities support the network
design: to generate and display nodes, to define their attributes
and to link them with oriented, symmetric or antisymmetric connections
of different weights. The editor can deal with large networks and provides some tools to
manage them easily, such as grouping facilities, that allow to deal with a net sub-part as
if it were just one object. The main window is provided with a main menu bar, at the top of the window, through which
users can manage the application. At the bottom of the window there is a tool panel,
where users can select some often used tools just by clicking on an icon button, to
allow a faster interaction.
The network is displayed in the editing area. Neurons are shaped as spheres of different dimensions: yellow if they are active
and purple if they are non-active (the activation threshold is conventionally set
to 0.5); neurons have an optional text label, which can be used to single out
relevant neurons, such as output neurons.
Arcs are shaped as segments connecting two neurons: arrows may be present to indicate arc
type (see the STANDARD and CONNECTIONS modes). Arcs connecting a node with itself (loop
connection) will appear as a circle starting and ending from the node. Arcs color is yellow if
their weight is positive and light blue if their weight is negative or null.
When the application is run, the standard mode of operating in the
main window is automatically entered and can be changed to accomplish different tasks.
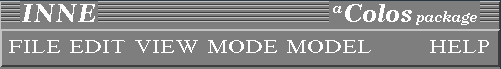
It represents INNE main menu and lists several items: FILE,
EDIT, VIEW, MODE, MODEL, HELP.
Each item has a submenu. All selections in the menu bar or submenus and actions
are carried over by pushing and releasing the mouse left button, except when
otherwise explicitely stated.
-
FILE
- It contains five options:
NEW, LOAD, SAVE, NOTEPAD and QUIT.
NEW
- allows the editing of a brand new net, erasing the current one, if any; a safety control prevents from loosing a network by mistake.
LOAD and SAVE
- allow loading pre-existing net files and saving current net; the file selections
are possible using a standard Motif file selection box (cfr. X-Window reference manual).
Each file records the net internal structure and its graphical representation in a given
format. Loading a file erases the current net, if any; a safety control prevents from loosing a network by mistake.
NOTEPAD
- opens an indipendent window for text editing: a scrollable text window provided with buttons
SAVE, LOAD, CLEAR and CLOSE. It is used to enclose a note file to the net, but also to manage any text file using a standard Motif interface. Note file are not saved on disk without an explicit SAVE operation. Closing the notepad window will
not change its content, wich remains in its memory buffer: only CLEAR or a further LOAD
operation will overwrite it.
QUIT
- obviously causes quitting the application; a safety control prevents from loosing a net by mistake.
-
EDIT
- Provides access to the usual graphical editing facilities. The submenu has the following
options:
DEFAULTS, CUT, PASTE, COPY and RESET NET.
DEFAULTS
- opens an options box to set some editing defaults: the
NEURONS STATE is the state
value that neurons assume at creation time. Two Motif toggle buttons (cfr. X-Window reference
manual) allow to choose new ARCS WEIGHT: either fixed or random value. If FIXED WEIGHTS is set, the weight of a new arc has the value showed as ARCS WEIGHT; if RANDOM WEIGHTS is set, the weight of a new arc has a random value in the interval [x,y], where
x = ARCS WEIGHT-ARCS WEIGHT RANGE and y = ARCS WEIGHT+ARCS WEIGHT RANGE; setting these options effect only objects that will be created afterwards.
CUT
- allows users to erase selected neurons and arcs (high-lighted in green) from a
network. Cutting implies that erased objects are kept in a buffer,
except for erased arcs linking two neurons which have not been both selected.
The buffer content is available for further operations, such as pasting the objects in a
different position in the network.
PASTE
- allows users to select a position in the network and then to copy the buffer
content, namely to add neurons and arcs to the network.
Selecting this functionality changes the cursor shape, which becomes a little cross; one can
move the mouse sprite until it is on the desired pasting position; a rectangle dragged by
the pointer will show the extension that the pasted objects will have; a copy of the buffer
content will be drawn upon pushing the left mouse button. This operation can be performed
several times, until another functionality is selected.
COPY
- causes the copy of the selected neurons and arcs into the buffer, without performing
any other operation on the objects. One has to use the
PASTE functionality later, to add
the buffer content in a different position on the network.
RESET NET
- resets neurons state and arcs weight for the current net; the new values assumed
are the current editing default values; it provides a fast way to change net global status.
-
VIEW
- It allows users to customize some graphical layout options; the submenu has the
following items:
DEFAULTS, HIDE/SHOW ARCS and REFRESH.
DEFAULTS
- opens an options box to set some graphical view defaults: users can define the
editing area dimensions setting the
AREA WIDTH and AREA HEIGHT values; this feature allows to edit a net
in an area wider than the editing area in the main application window, using two Motif scrolling
bars (cfr. X-Window reference manual) users can draw over the whole area. The NEURONS
MARGIN is the distance between neurons when they are created in group with a matrix layout
(see also NEURONS, the mode to create neurons, in the mode menu).
HIDE/SHOW ARCS
- toggles arcs visibility, that makes
all arcs visible or not. This feature is useful whenever it is necessary to pay
attention mainly at the neuron states and showing all connections would be confusing.
REFRESH
- redisplays the application windows; useful in case of expose faults.
-
MODE
- It provides access to different net editing tools, which are also available from the
quick tools panel in the bottom of the main window. A submenu lists six different options:
NEURONS,
CONNECTIONS, ERASE, CLAMP, STANDARD and SET.
Choosing one of them implies a mode selection, which will be changed only by selecting
another one from the submenu; each mode implies the change of the cursor shape, for users
convenience.
NEURONS
- option enters the neuron creation mode. The mouse sprite will be a neuron;
positioning the mouse anywhere on the edit area and pushing the left button will
cause the generation of a new neuron, whose initial values, state or threshold,
will be set according to the current editing parameter values. See
EDIT DEFAULTS
in the edit menu for details.
Users can also create many neurons simultaneously: pushing the middle button
and moving the mouse will drag a rectangle filled of arranged neuron shapes;
releasing the middle button will create the shown neurons, with a matrix layout;
a popup label shows, at any time, the number of neurons (rows x columns) that user is
going to create.
CONNECTIONS
- option sets the arc creation mode. It allows to choose the connection type of
a new arc: oriented, that is a link that has a source
node and an object node and that therefore has a direction; symmetric, that is a
link that connects two neurons both ways with the same weight; and antisymmetric,
that is a link that connects two neurons both ways, but has a weight in a direction
and the opposite in the other one. In this mode the mouse sprite will be changed
to a cross, with the kind of connection represented by the number
of arrows, zero, one or two, which are shown on the cross. The starting node of a new link
is set clicking on a first neuron; then moving the mouse around will
drag a line that will become the link after a second neuron
will be chosen. Clicking the mouse button in a
position where no neuron is found, causes no action and the first neuron selection
is ignored. Once created a connection, there will be an arrow showing the direction if
it is oriented, no arrow if it is symmetric, two arrows if it is antisymmetric.
Selecting a single neuron or a neuron currently grouped with other objects
(highlighted in green) will perform a quite analogous action: clicking on a first
object will cause the pointer to drag a line starting from each selected neuron; on the
other hand, clicking on a second object will connect all the selected neurons
with the first neuron (or group of neuron, of course). The option of grouping
neurons with the middle button (see the
STANDARD mode) is active in this mode too, to allow
fast and powerful links editing.
ERASE
- option sets the erase mode, which enables to delete objects from the
network. The cursor will be shaped as a waste basket. In this mode when clicking
on a node, it will be erased together with all its connections. To delete an arc,
one has to click on the little mark in the middle of it. This mode is similar to
the edit function
CUT, except that it does not copy deleted objects in the buffer.
As well as in neurons and connections mode, also in this mode users can select a back-error propagation doesn't use it). In this mode, a button
click on a neuron will toggle its clamp property.
STANDARD
- is the default mode: the cursor shape as the default one (generally an
arrow) and all three mouse buttons are active.
- Left button
- opens a panel related to neurons or arcs, to set their attributes.
For a neuron, users can define its state value, its class, choosing between
INPUT, OUTPUT and HIDDEN unit (some neural models use this information
to drive learning and computation) and its label to single out a neuron on screen.
For an arc, users can define arc weight and arc type setting.
Clicking left button on a neuron belonging to a selected group, will open a neuron panel, but the settings will be applied to all the selected neurons.
In the panels buttons OK and CANCEL, allows to apply the new settigs or to restore the old ones.
- Middle button
- in standard mode performs the selection of objects in the screen.
To select a group of objects (neurons and arcs), one has to click on the middle mouse
button in a point in the background, where there isn't any neuron or arc, and drag the
mouse pointer, without releasing the button: a green rectangle will be drawn,
following the mouse position. Releasing the mouse middle button will cause all the objects
completely included in the rectangle to be selected as a group and to be highlighted in
green. A single object selection can also be done, pushing the middle button just on the
wanted object. The selected group is ready to be used as input to the editing
functions: cut, paste, copy, erase, attributes setting, and so on. Note that a further
group selection will overwrite the first, so to unselect a group, one
can simply click the mouse middle button in the background.
When objects to be selected are scattered in the editing area and can not be included in a single rectangulare area,
a multiple selection must be done, holding the SHIFT key pressed while performing the
required selections: if the SHIFT key isn't down, each selection will erase the last one.
- Right button
- performs the action of moving neurons around in the editing area.
If you want to move a neuron, or a neuron group, push the right mouse button while you are
on it and then, holding the button down, move the mouse to a new position where you
release the button. When moving a single neuron, the arcs linked to it will follow it.
Otherwise, when moving a group, one will see moving only a green
rectangle, representing the group bounding box, and only after button is released
the group will be drawn in the new position.
SET
- option allows users to specify neuron boolean values: the user can select between the
on state, represented by the float value 1.0, and the off state, represented by the
float value 0.0. In this mode, clicking on a neuron with the left mouse button, will set
the on neuron state; a middle button click will toggle the state on/off; at last, a
right button click will set the off neuron state.
This mode is associated to the mouse motion too: holding down any button and moving
the pointer will perform the relative action on the state of all the crossed neurons.
-
MODEL
- It provides the list of the neural network models, which have been implemented in the
environment. Choosing a model, causes the opening of a dialog panel. The network
layout, presently shown in the main window aditing area has to be associated to a model,
before any computation can take place.
In the present version the following models are implemented:
Boltzmann machine,
the Back-error propagation model, the Hebb's rule model, the Simple competitive model and the
Kohonen feature map.
See the specific manual sections for detailed informations.
-
HELP
- INNE manual is accessible from this menu, as an HTML file. You can also recall from this menu the HTML files describing the models that have been implemented.

The quick tool panel is located at the bottom of the main window.
It shows the icons of the most frequently used modes or actions during an editing session. One can select a
mode or execute an action, clicking the left mouse button when its pointer is over one of
the icon buttons.
 It is equivalent to select
It is equivalent to select NEURONS in the MODE
menu.
 Icons used to select the arc creation mode according to arc types: symmetric (no arrows), oriented (one arrow) and antisymmetric (two arrows) connections. This mode is equivalent to select the connection type from the submenu
Icons used to select the arc creation mode according to arc types: symmetric (no arrows), oriented (one arrow) and antisymmetric (two arrows) connections. This mode is equivalent to select the connection type from the submenu
CONNECTIONS in the MODE menu.
 It is equivalent to select
It is equivalent to select ERASE in the MODE menu.
 Icon used to choose the clamp toggle mode: it is equivalent to select
Icon used to choose the clamp toggle mode: it is equivalent to select CLAMP in the MODE menu.
 It is equivalent to select
It is equivalent to select STANDARD in the MODE menu.
 It is equivalent to select
It is equivalent to select SET in the MODE menu.
 Icons used to change the size of the neuron to be created; the first button
increases the size, the second one decreases it. These actions are useful when the
net has a large number of nodes to be displayed, so smaller neuron images will save space.
Icons used to change the size of the neuron to be created; the first button
increases the size, the second one decreases it. These actions are useful when the
net has a large number of nodes to be displayed, so smaller neuron images will save space.
 Back to index
Back to index
 It is equivalent to select
It is equivalent to select 



 It is equivalent to select
It is equivalent to select  Icons used to select the arc creation mode according to arc types: symmetric (no arrows), oriented (one arrow) and antisymmetric (two arrows) connections. This mode is equivalent to select the connection type from the submenu
Icons used to select the arc creation mode according to arc types: symmetric (no arrows), oriented (one arrow) and antisymmetric (two arrows) connections. This mode is equivalent to select the connection type from the submenu
 It is equivalent to select
It is equivalent to select  Icon used to choose the clamp toggle mode: it is equivalent to select
Icon used to choose the clamp toggle mode: it is equivalent to select  It is equivalent to select
It is equivalent to select  It is equivalent to select
It is equivalent to select  Icons used to change the size of the neuron to be created; the first button
increases the size, the second one decreases it. These actions are useful when the
net has a large number of nodes to be displayed, so smaller neuron images will save space.
Icons used to change the size of the neuron to be created; the first button
increases the size, the second one decreases it. These actions are useful when the
net has a large number of nodes to be displayed, so smaller neuron images will save space.
 Back to index
Back to index