
An example of application of Hebbian learning rule to image compression
The proliferation of multi-media tools in computer
communication networks has increased the demand for
techniques to improve the efficiency of transmission and
storage of image; so a large variety of algorithm for image
compression has been realized.
The basic idea behind a class of image compression algorithms
is to exploit the fact that nearby pixels in images are often
highly correlate. A given image is therefore divided into several
blocks of pixels, and each block (treated as vector) is linearly
transformed into a vector whose component are mutually
uncorrelated. These components are then independently
quantized for transmission or storage. The reconstruction of the
original image is obtained by using an inverse linear transform
operation on the quantized coefficient vector.
The optimal transform in which the average mean-squared
reconstruction error is minimized is called Principal
Component Analysis (or Karhunen-Loeve transform).
Image compression process consists of two phases:
- The image is used to train the network;
- With the trained network the image is compressed;
1. The network has mxn input neurons fully connected with k
output neurons. The image to be compressed is divided into blocks of pixels
with size mxn. The image is scanned from left to right and top to
bottom, and these vectors are consecutively presented to the input units of
the network.

2. The image is compressed by multiplying each block represented as a N-dimensional
vector by each of the M weight vectors obtained after training to
generate M coefficients for coding the block. Assuming that each block
consists of pxp pixels, the coefficients for the block
bn,m starting at position (n*p+1,m*p+1) in the image
I are given by:
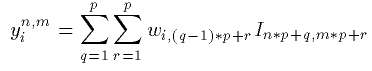
This values are a compressed representation of the original image.
To reconstruct the image from the yi this rule
is used:
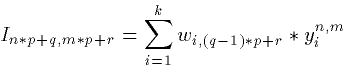
where k is the number of the output neurons.


This is an example of image compression: the first is the original image, the
second is the same image compressed and then reconstructed.
 Back to index
Back to index



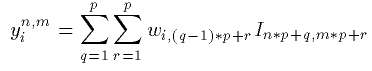
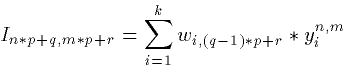


 Back to index
Back to index